In pig production, the impact of pig diseases on profits is huge, and the impact is usually greater when clinical diseases break out. Early infection will have a negative impact on the weaning weight and weight of pigs at the end of nursing. In addition, light-weight pigs are prone to diseases in the later stages of breeding. Some important pathogens in the critical stages of pig production (parturition and nursing) are: Staphylococcus suis, Streptococcus, Haemophilus parasuis, Pasteurella multocida, etc.

When it comes to the above diseases, one of the most commonly used drugs in pig farms is amoxicillin. In pig production, amoxicillin is popular among pig farmers because of its many dosage forms, such as intramuscular injection, drinking water and mixing with feed, large dosage, small side effects, good effect and low price. However, we also found that there are places where pig farms are improperly used in pig farms. Today, the dosage and usage of amoxicillin are summarized as follows, which I believe will be helpful to our pig production.
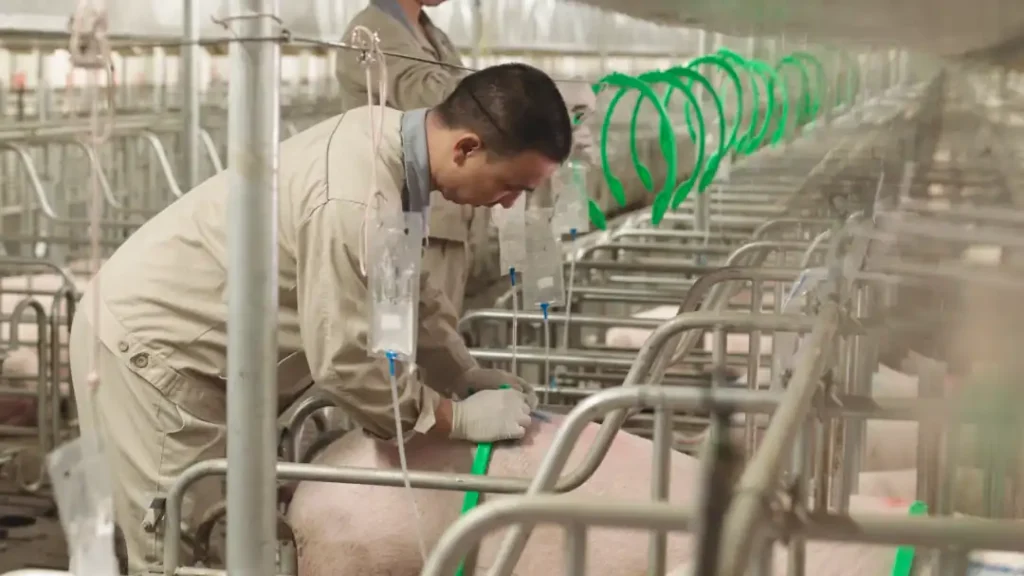

1, Amoxicillin is commonly used in the following aspects
1. Early infection of Streptococcus suis, Pasteurella and Haemophilus parasuis, and Staphylococcus aureus in pigs (amoxicillin + dexamethasone intramuscular injection) has obvious effects.
2. Treatment of yellow and white diarrhea and swine erysipelas in piglets.
3. Used for systemic infection of sows and postpartum anti-inflammatory.
2, Calculation of the amount of amoxicillin powder mixed with feed
Assuming that the oral dose of amoxicillin is 6 mg/kg body weight, the pig weighs 50 kg, and the daily feed intake is 3 kg, then: Amoxicillin dosage = 6X50 = 300 mg Mixed feed ratio = 300 mg/3 kg = 100 ppm, that is, 100 grams of pure amoxicillin is added per ton of feed.
At present, amoxicillin preparations are generally 10% powder, so 1 kg of 10% amoxicillin should be used per ton of feed to prevent general bacterial diseases. This is also the recommended dose of many veterinary pharmaceutical factories.
The above calculation is for growing pigs. For sows, the dosage should be increased to 2-3 kg/ton of feed for best results.
3, 10% Amoxicillin: Is 1 kg/ton of feed enough?
In fact, pig farms only use this dosage for disease prevention, and the actual treatment dosage is often higher. Due to people’s concerns about drug resistance (which is true), amoxicillin preparations are relatively cheap and very safe. Therefore, adding 10% amoxicillin to 2-3 kg/ton of feed is more effective in disease control.
Here we introduce the difference between amoxicillin mixed with feed and drinking water for the convenience of pig farmers.
Treatment with feed There are two main advantages of adding amoxicillin to feed:
(1) Less labor can be used to treat a large number of pigs. Using drugs to treat large groups of animals is very time-consuming, and mixing drugs in feed is a very suitable method.
(2) Consistency. If a treatment needs to last for several days, adding the drug to the feed will reduce the probability of missing some pigs.
However, feed-based treatment has some disadvantages:
(1) Duration of action. It may take several days until all animals receive the drug. When an outbreak occurs, the drug-added feed must be ordered and sent to the pig farm. Finally, the feed tank must be empty before the drug is administered.
(2) Feed intake. The health of the pigs will affect feed intake, and a certain percentage of pigs may not eat enough feed to get enough drug.
(3) Manufacturing issues. Although there are different products on the market, the stability of the amoxicillin molecule can be affected by feed pelleting. In addition, when the feed is mixed, premix segregation often occurs, resulting in different drug doses in the same batch of feed.
(4) Risk of intestinal microecological imbalance. When amoxicillin (or other antibiotics) are taken orally, intestinal dysbiosis may occur, resulting in impaired intestinal health of piglets.
Drinking water use Some advantages of drinking water use are similar to those of feed-based treatment:
(1) Treating large numbers of pigs. Drinking water treatment can treat a large number of pigs at one time with less labor, but it is also important to pay attention to timely and more accurate dosing.
(2) Targeted treatment. Targeted treatment can be carried out on a pig house basis, or even on different pens within the same house. In addition, the duration of treatment can be based on need, unlike feed dosing, where the animals are treated until the feed tank is empty.
(3) Follow-up treatment. Amoxicillin dissolved in water is a very effective follow-up treatment measure, which is particularly important during disease outbreaks. Timely treatment doses (using injection doses) dissolved in water can maintain the drug concentration in the pig’s blood at a good level and can last for several days.
At the same time, drinking water dosing has some disadvantages, including:
(1) Dosage and treatment consistency. Generally speaking, drinking water dosing is not as uniform as feed dosing, but this can be improved through improved equipment and training.
(2) Low pH. Some pig farms have low water pH or use acidifiers. Amoxicillin’s solubility is affected in acidic water, and according to one study, it reacts with citric acid to form white precipitates or crystals.
(3) Water intake. The health of the pig also affects water intake. In addition, there is evidence that diarrhea caused by E. coli reduces the absorption of amoxicillin on the first day of drinking water administration.
Choosing the best method
In the early stages of pig production, some important pathogens are bacteria that can be treated with amoxicillin. Like most antibiotic treatments, there are many factors to consider when deciding which method of administration to use. Each pig farm and each situation must consider which method of administration is more appropriate.
4, Drug interactions
The combination of amoxicillin and carbaspirin calcium can delay absorption and excretion from the kidneys, thereby improving the efficacy to a certain extent. However, it stays in the stomach for a long time, and gastric acid may destroy part of the drug. Overall, it is a wiser choice to use a high-quality and stable amoxicillin preparation.
The combination of amoxicillin and clavulanic acid can improve the efficacy and enhance the effect.
5, Precautions
Although amoxicillin is a good drug, you still need to be very careful when using it. Choose different methods of use according to the different conditions of pigs to best exert the efficacy of amoxicillin.
It is generally better to administer amoxicillin in drinking water within 3 hours. Too long administration time will cause the efficacy to be reduced or ineffective! Practical experience in using amoxicillin in pig production shows that no matter which method of use, you need to pay attention to details to achieve success.